Understanding Stroke: Warning Signs & Prevention
- 13th March 2025
Introduction
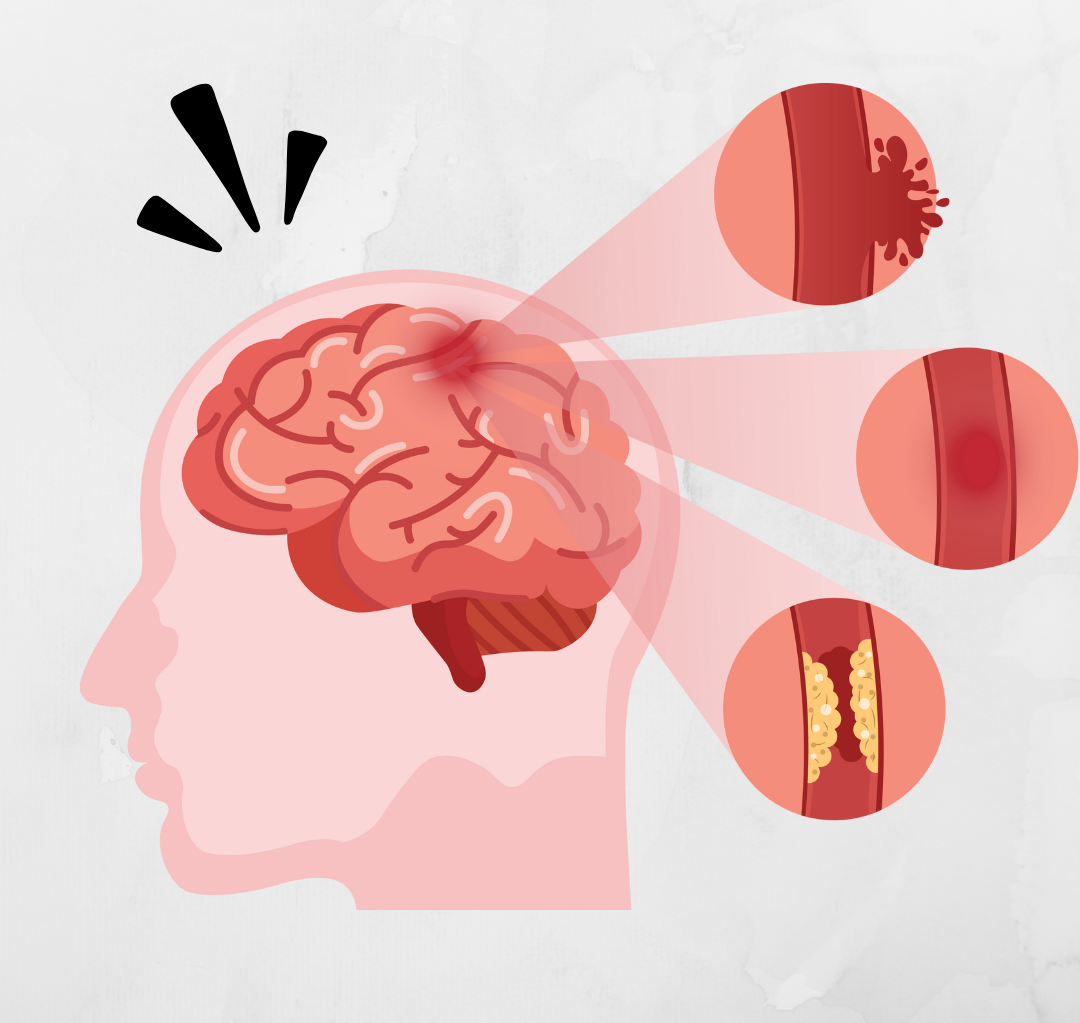
A stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain cells of oxygen. It is one of the leading causes of disability and death worldwide, but the good news is that many strokes can be prevented. Recognizing the warning signs early can save lives and improve recovery outcomes.
What is a Stroke?
A stroke happens when there is a sudden disruption in the blood flow to the brain. This can be caused by a blockage (ischemic stroke) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). In some cases, a transient ischemic attack (TIA), often called a "mini-stroke," serves as a warning sign of a major stroke.
Common Warning Signs of Stroke
Recognizing stroke symptoms early and seeking immediate medical attention can significantly reduce damage to the brain. The FAST acronym is a simple way to remember the key symptoms:
F - Face Drooping: Does one side of the face droop, or is it numb? Ask the person to smile and check for asymmetry.
A - Arm Weakness: Is one arm weak or numb? Ask them to raise both arms and see if one drifts downward.
S - Speech Difficulty: Is speech slurred or hard to understand? Ask them to repeat a simple sentence.
T - Time to Call Emergency Services: If any of these symptoms appear, seek medical help immediately.
Other symptoms may include sudden confusion, vision problems, dizziness, loss of balance, or a severe headache with no known cause.
Stroke Prevention: How to Reduce Your Risk
Although some risk factors like age and family history cannot be changed, many lifestyle adjustments can significantly lower your stroke risk.
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce salt and saturated fat intake to keep blood pressure in check.
Exercise Regularly: Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to keep your heart and blood vessels healthy.
Control High Blood Pressure: Monitor your blood pressure regularly and follow your doctor's advice to keep it within a healthy range.
Manage Diabetes: Keep blood sugar levels under control with proper diet, medication, and regular monitoring.
Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke by damaging blood vessels and reducing oxygen levels in the blood.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to high blood pressure and an increased risk of stroke.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to higher risks of stroke, so aim for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Monitor Cholesterol Levels: High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of a stroke.
Manage Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure and unhealthy habits that increase stroke risk. Practice mindfulness, meditation, or other stress-reducing techniques.
Conclusion
A stroke can be life-threatening, but recognizing the warning signs and taking preventive steps can make a significant difference. By adopting a healthier lifestyle and managing risk factors, you can reduce the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Stay informed, spread awareness, and take action today to protect your brain health.
If you or someone you know is experiencing stroke symptoms, seek immediate medical attention—every second counts! For more details visit